AG Scientific is a leading supplier of high-quality reducing agents for all life science and research applications, including DTT and TCEP HCl. Here we discuss the basic differences between these two popular reducing agents.
TCEP Hydrochloride
Product:
- TCEP Hydrochloride (CAS 51805-45-9)
Description:
TCEP HCl has the advantages of being odorless, more powerful, irreversible, more hydrophilic, and more resistant to oxidation in air. Near complete reduction of disulfide bonds.
Alternative Name:
Tris(2-Carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride
Molecular Weight
286.6 Da
Chemical Formula:
C9H16O6PCl
Chemical Structure:
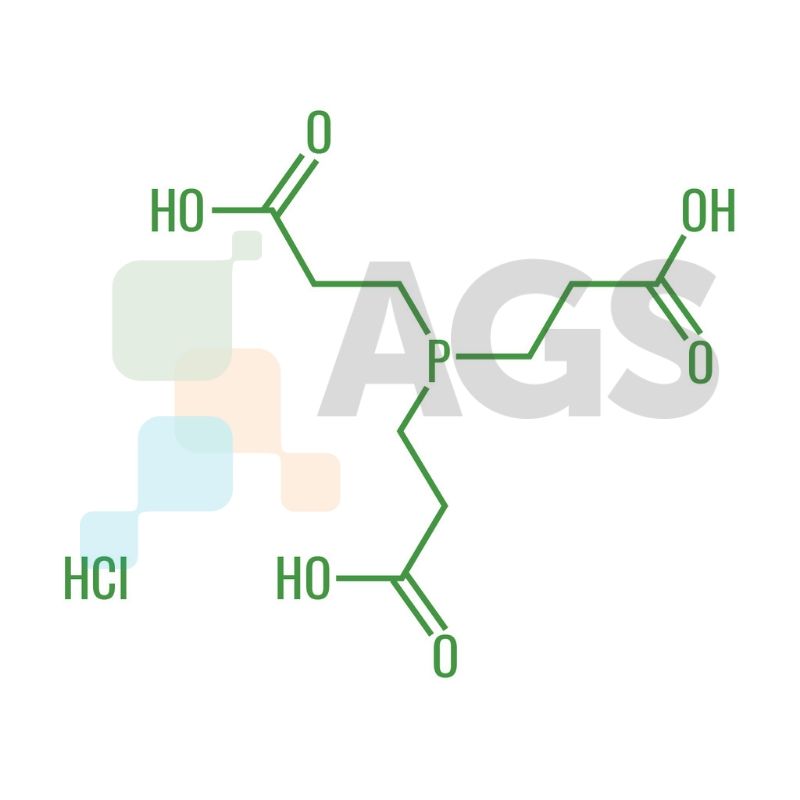
Appearance:
Odorless, white crystals
Solubility:
310 g/L
Degradation:
TCEP is not very stable in phosphate buffers, especially at neutral pH. Since TCEP is charged in solution, it is not compatible for use in isoelectric focusing.
Effective pH:
Effective at lower/wider pH. Effective pH range is 1.5 to 8.5. When dissolved in water resulting pH is ~2.5.
Removal Requirements:
TCEP removal is not required prior to most applications (e.g. histidine-tagged protein purification, maleimide conjugations).
Applications:
Popular for Protein applications, SDS-PAGE, mass spectrometry applications, TCEP does not reduce metals used in immobilized metal affinity chromatography. TCEP is often used as a reducing agent to break disulfide bonds within and between proteins as a preparatory step for gel electrophoresis, histidine-tagged protein purification, maleimide conjugations.
DTT [dithiothreitol]
Product:
- DTT [dithiothreitol] (CAS 3483-12-3)
Description:
DTT is a protective agent for reducing S-S TO SH groups. Used as a strong reducing agent for proteins and enzymes.
Alternative Name:
Cleland's Reagent
Molecular Weight:
154.25 Da
Chemical Formula:
C4H10O2S2
Chemical Structure:
![Chemical structure of DTT [dithiothreitol]](/system/user_files/Images/C-1029%20structure%20AGS.jpg)
Appearance:
Slight sulfur smell, white crystalline powder
Solubility:
50 g/L
Degradation:
Yes, when stressed at 30ºC, DTT demonstrates degradation starting after 3 days and increasing rapidly after 5 days. Sensitive to nickel.
Effective pH:
Reducing power is limited to pH values >7. Redox potential is -0.33 V at pH 7.
Removal Requirements:
DTT is removed by filtration (for the solid catalyst) or by chromatography (for the liquid form).
Applications:
DTT is as a reducing or “deprotecting” agent for thiolated DNA. Electrophoresis.
Additional Reading:
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) Applications You Must Know
- 20 DTT (Dithiothreitol) FAQs
- Dithiothreitol AKA Cleland’s Reagent

